명품 C++ 프로그래밍::3장 실습과제
3장 실습문제
1.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Tower{
int height;
public:
Tower(){ height = 1; }
Tower(int h){ height = h; }
int getHeight(){ return height; }
};
int main()
{
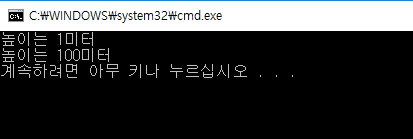
Tower myTower;
Tower seoulTower(100);
cout << "높이는 " << myTower.getHeight() << "미터" << endl;
cout << "높이는 " << seoulTower.getHeight() << "미터" << endl;
return 0;
}
2.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Date{
int year, month, day;
public:
Date(int y, int m, int d){ year = y, month = m, day = d; }
Date(char *s);
void show(){ cout << year << "년" << month << "월" << day << "일" << endl; }
int getYear(){ return year; }
int getMonth(){ return month; }
int getDay(){ return day; }
};
Date::Date(char *s){
char a[20];
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(s); i++)
a[i] = *(s + i);
year = atoi(strtok(a, "/"));
month = atoi(strtok(NULL, "/"));
day = atoi(strtok(NULL, ""));
}
int main()
{
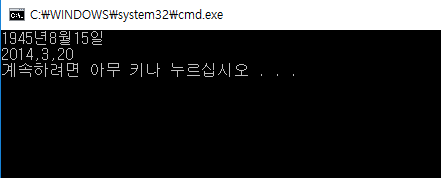
Date birth(2014, 3, 20);
Date independenceDay("1945/8/15");
independenceDay.show();
cout << birth.getYear() << ',' << birth.getMonth() << ',' << birth.getDay() << endl;
return 0;
}
3.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
class Random{
public:
Random(){ srand((unsigned)time(0)); }
int next();
int nextInRange(int min, int max);
};
int Random::next(){
int num = rand();
return num;
}
int Random::nextInRange(int min, int max){
int num = rand() % (max - min + 1) + min;
return num;
}
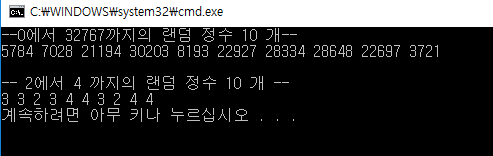
int main()
{
Random r;
cout << "--0에서 " << RAND_MAX << "까지의 랜덤 정수 10 개--" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
int n = r.next();
cout << n << ' ';
}
cout << endl << endl << "-- 2에서 " << "4 까지의 랜덤 정수 10 개 --" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
int n = r.nextInRange(2, 4);
cout << n << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
4.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
class EvenRandom {
public:
EvenRandom() { srand((unsigned)time(0)); }
int next();
int nextInRange(int min, int max);
};
int EvenRandom::next() {
int num;
while (1) {
num = rand();
if (num % 2 == 0) break;
}
return num;
}
int EvenRandom::nextInRange(int min, int max) {
int num;
while (1) {
num = rand() % (max - min + 1) + min;
if (num % 2 == 0) break;
}
return num;
}
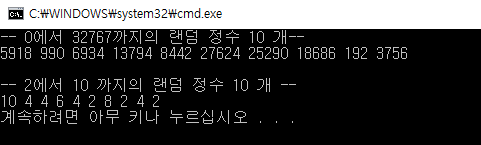
int main()
{
EvenRandom r;
cout << "-- 0에서 " << RAND_MAX << "까지의 랜덤 정수 10 개--" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int n = r.next();
cout << n << ' ';
}
cout << endl << endl << "-- 2에서 " << "10 까지의 랜덤 정수 10 개 --" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int n = r.nextInRange(2, 10);
cout << n << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
5.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
class SelectableRandom{
public:
SelectableRandom(){ srand((unsigned)time(0)); }
int next();
int nextInRange(int min, int max);
};
int SelectableRandom::next() { //EVEN
int num;
while (1) {
num = rand();
if (num % 2 == 0) break;
}
return num;
}
int SelectableRandom::nextInRange(int min, int max) { //ODD
int num;
while (1) {
num = rand() % (max - min + 1) + min;
if (num % 2 != 0) break;
}
return num;
}
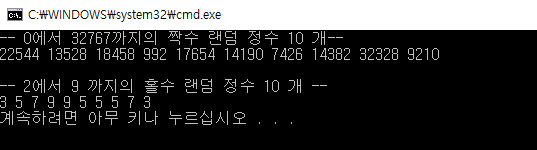
int main()
{
SelectableRandom r;
cout << "-- 0에서 " << RAND_MAX << "까지의 짝수 랜덤 정수 10 개--" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int n = r.next();
cout << n << ' ';
}
cout << endl << endl << "-- 2에서 " << "9 까지의 홀수 랜덤 정수 10 개 --" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int n = r.nextInRange(2, 9);
cout << n << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
6.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Integer{
int num;
public:
Integer(int num){ this->num = num; }
Integer(string num){ this->num = stoi(num); }
int get(){ return this->num; }
void set(int num){ this->num = num; }
bool isEven() { if (num % 2 == 0) return true; else return false; }
};
int main()
{
Integer n(30);
cout << n.get() << ' ';
n.set(50);
cout << n.get() << ' ';
Integer m("300");
cout << m.get() << ' ';
cout << m.isEven();
return 0;
}

\
7.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Oval {
int width, height;
public:
Oval() { width = 1; height = 1; }
Oval(int w, int h) { width = w; height = h; }
~Oval() { cout << "Oval 소멸 : width = " << width << ", height = " << height << endl; }
int getWidth() { return width; }
int getHeight() { return height; }
void set(int w, int h) { width = w; height = h; }
void show() { cout << "width = " << width << ", height = " << height << endl; }
};
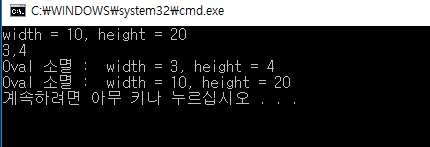
int main()
{
Oval a, b(3, 4);
a.set(10, 20);
a.show();
cout << b.getWidth() << "," << b.getHeight() << endl;
return 0;
}
8(1)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Add {
int a, b;
public:
void setValue(int x, int y) { a = x; b = y; }
int calculate() { return (a + b); }
};
class Sub {
int a, b;
public:
void setValue(int x, int y) { a = x; b = y; }
int calculate() { return (a - b); }
};
class Mul {
int a, b;
public:
void setValue(int x, int y) { a = x; b = y; }
int calculate() { return (a * b); }
};
class Div{
int a, b;
public:
void setValue(int x, int y) { a = x; b = y; }
int calculate() { return (a / b); }
};
int main()
{
int x, y;
char op;
while (1) { //for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
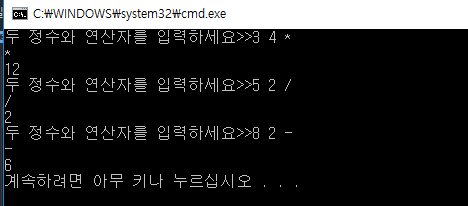
cout << "두 정수와 연산자를 입력하세요>>";
cin >> x >> y >> op;
cout << op<<endl;
switch (op) {
case '+':
Add add;
add.setValue(x, y);
cout << add.calculate() << endl;
break;
case '-':
Sub sub;
sub.setValue(x, y);
cout << sub.calculate() << endl;
break;
case '*':
Mul mul;
mul.setValue(x, y);
cout << mul.calculate() << endl;
break;
case '/':
Div div;
div.setValue(x, y);
cout << div.calculate() << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "잘못된 연산자" << endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
8(2)
클래스 선언부는 헤더파일에, 클래스 구현부는 cpp파일, main함수가 있는 파일은 main.cpp 파일에 나누어 작성한다.
9.
[Box.h]
#ifndef BOX_H_
#define BOX_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box {
int width, height;
char fill;
public:
Box(int w, int h) { setSize(w, h); fill = '*'; }
void setFill(char f) { fill = f; }
void setSize(int w, int h) { width = w; height = h; }
void draw();
};
#endif
[Box.cpp]
#include "Box.h"
void Box::draw() {
for (int n = 0; n < height; n++) {
for (int m = 0; m < width; m++)cout << fill;
cout << endl;
}
}
[main.cpp]
#include "Box.h"
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
int main()
{
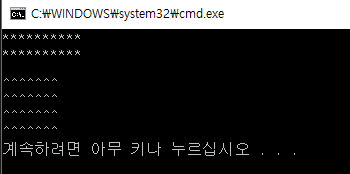
Box b(10, 2);
b.draw();
cout << endl;
b.setSize(7, 4);
b.setFill('^');
b.draw();
return 0;
}
10.
[Ram.h]
#ifndef RAM_H_
#define RAM_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Ram {
char mem[100 * 1024];
int size;
public:
Ram();
~Ram();
char read(int address);
void write(int address, char value);
};
#endif
[Ram.cpp]
#include "Ram.h"
Ram::Ram() {
size = 100 * 1024;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
mem[i] = 0;
}
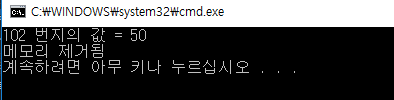
Ram::~Ram() {
cout << "메모리 제거됨 " << endl;
}
char Ram::read(int address) {
return mem[address];
}
void Ram::write(int address, char value) {
mem[address] = value;
}
[main.cpp]
#include "Ram.h"
int main() {
Ram ram;
ram.write(100, 20);
ram.write(101, 30);
char res = ram.read(100) + ram.read(101);
ram.write(102, res);
cout << "102 번지의 값 = " << (int)ram.read(102) << endl;
return 0;
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
피드백